What’s New?
Here is a (incomplete) log of the changes made to DEAP over time.
Release 0.9
- Major overhaul of the genetic programming with significant speed increase.
- Added state of the art operators to control bloat in GP.
- Several new examples from diverse fields.
- Examples are now compatible Python 2 and 3 out of the box.
- Organization of the examples.
Release 0.8
- Added forward compatibility to Python 3.2
- Replaced varSimple() and
varLambda() variation operators for the more specific
varAnd() and varOr()
operators.
- Added a logging facility (EvolutionLogger) that produce
easier to read console logging and a utility to transform that output into a
Python dictionary.
- Introduced the exact NSGA-II algorithm as described in Deb et al., 2002, A
Fast Elitist Multiobjective Genetic Algorithm: NSGA-II.
- NSGA-II selection algorithm revisited :
- Added a C++ version;
- Speed up of the Python version (up to 5x when the objectives are discrete).
- Added some new benchmarks (multiobjective, binary and moving peaks).
- Added translation, rotation, scaling and noise decorators to enhance benchmarks.
Release 0.7
- Modified structure so that DTM is a module of DEAP.
- Restructured modules in a more permanent and coherent way.
- The toolbox is now in the module base.
- The operators have been moved to the tools module.
- Checkpoint, Statistics, History and Hall-of-Fame are now also in the tools module.
- Moved the GP specific operators to the gp module.
- Renamed some operator for coherence.
- Reintroduced a convenient, coherent and simple Statistics module.
- Changed the Milestone module name for the more common Checkpoint name.
- Eliminated the confusing content_init and size_init keywords in the toolbox.
- Refactored the whole documentation in a more structured manner.
- Added a benchmark module containing some of the most classic benchmark functions.
- Added a lot of examples again :
- Differential evolution (x2);
- Evolution strategy : One fifth rule;
- k-nearest neighbours feature selection;
- One Max Multipopulation;
- Particle Swarm Optimization;
- Hillis’ coevolution of sorting networks;
- CMA-ES
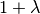 .
.
Release 0.6
- Operator modify in-place the individuals (simplify a lot the algorithms).
- Toolbox now contains two basic methods, map and clone that are useful in the algorithms.
- The two methods can be replaced (as usual) to modify the behaviour of the algorithms.
- Added new module History (compatible with NetworkX).
- Genetic programming is now possible with Automatically Defined Functions (ADFs).
- Algorithms now refers to literature algorithms.
- Added new examples :
- Coevolution;
- Variable length genotype;
- Multiobjective;
- Inheriting from a Set;
- Using ADFs;
- Multiprocessing.
- Basic operators can now be enhanced with decorators to do all sort of funny stuff.
Release 0.5
- Added a new module Milestone.
- Enhanced Fitness efficiency when comparing fitnesses.
- Replaced old base types with python built-in types.
- Added an example of deriving from sets.
- Added SPEA-II algorithm.
- Fitnesses are no more extended when assigning value, the values are simply assigned.
 .
.